Newsletter Subscribe
What are Amino Acids
Proteins play countless roles throughout the biological world.
Some transport nutrients throughout the body.
Some help chemical reactions to happen at faster rates,
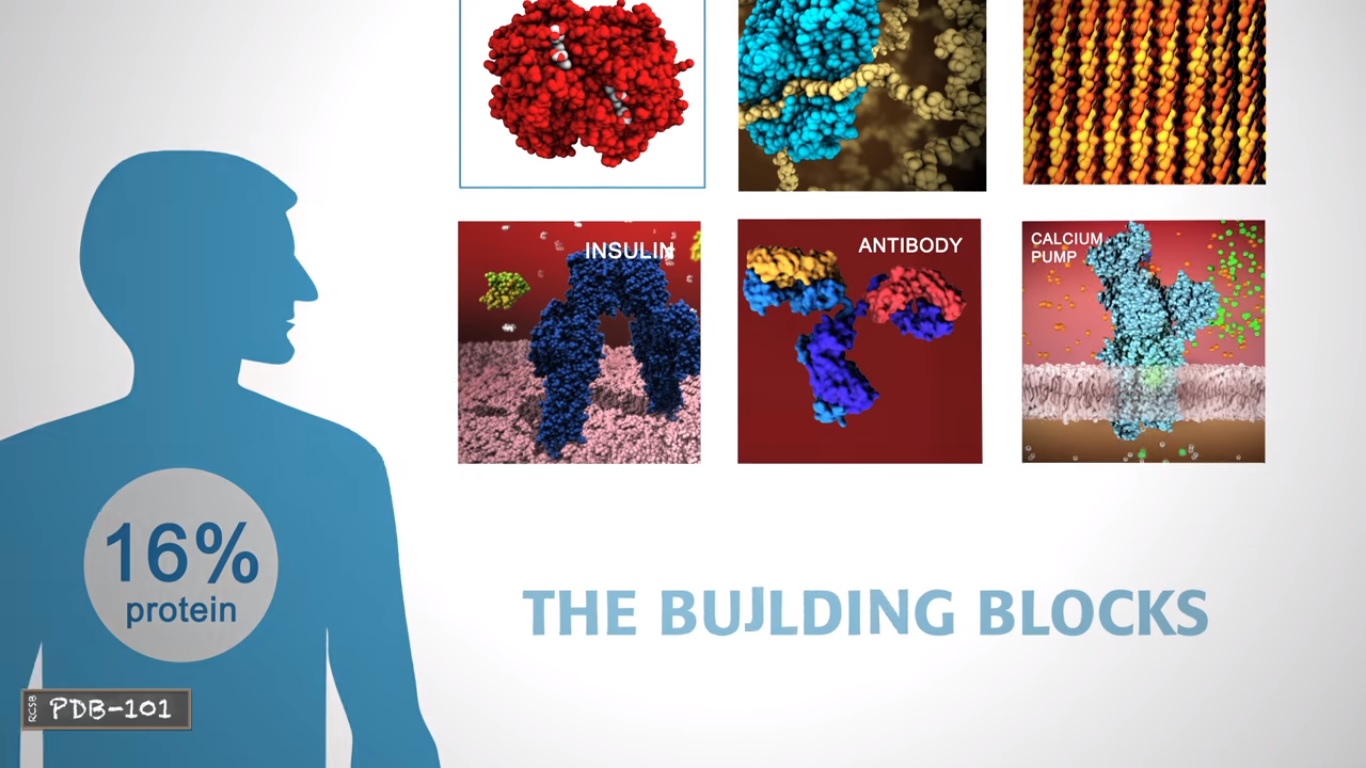
Others build structures that make up living things despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty one building blocks called amino acids.
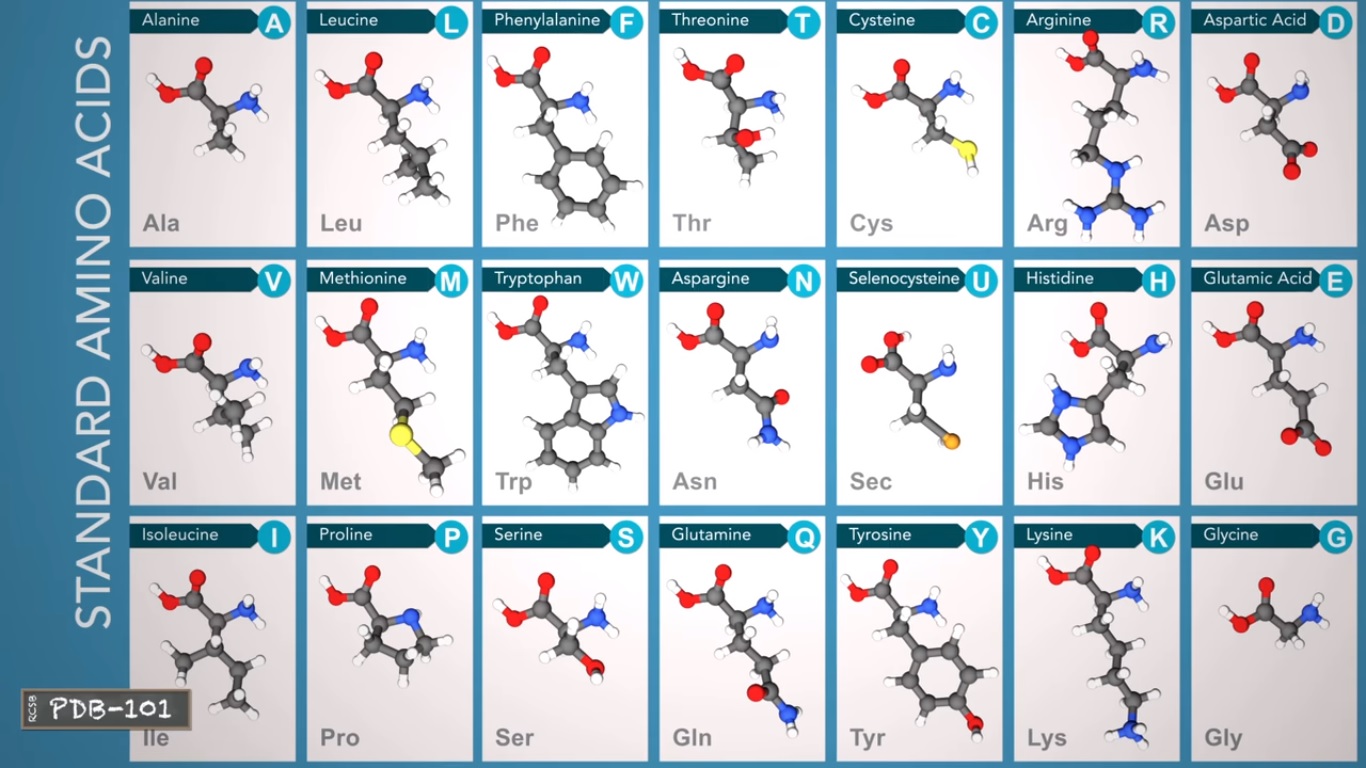
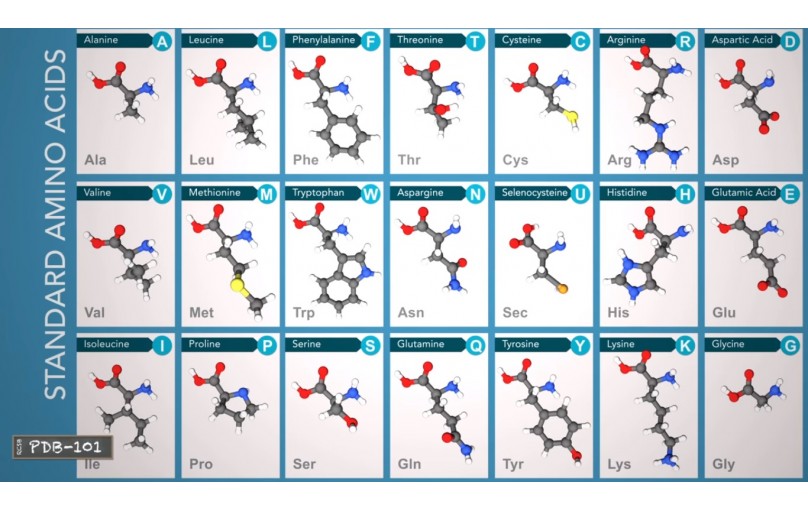
Amino acids are made of carbon oxygen nitrogen and hydrogen atoms and some contains sulfur atoms.
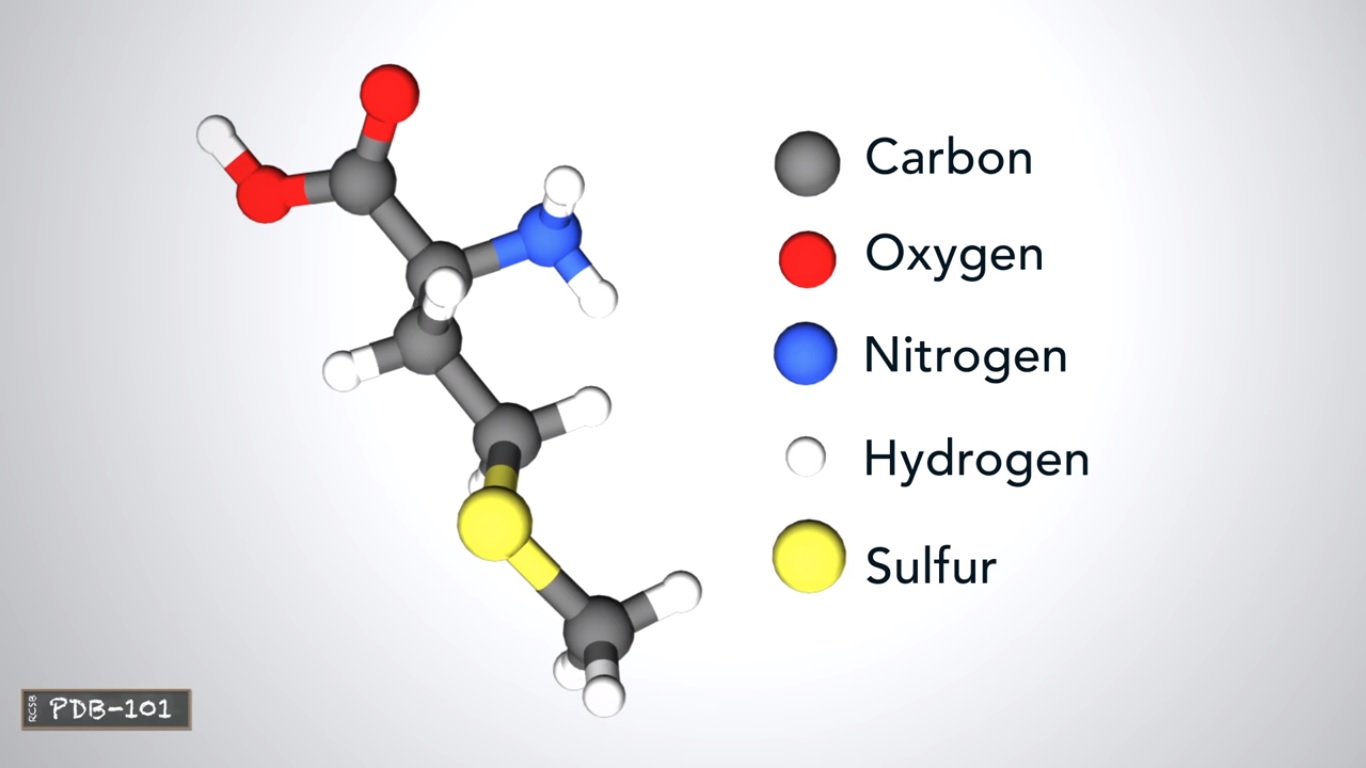
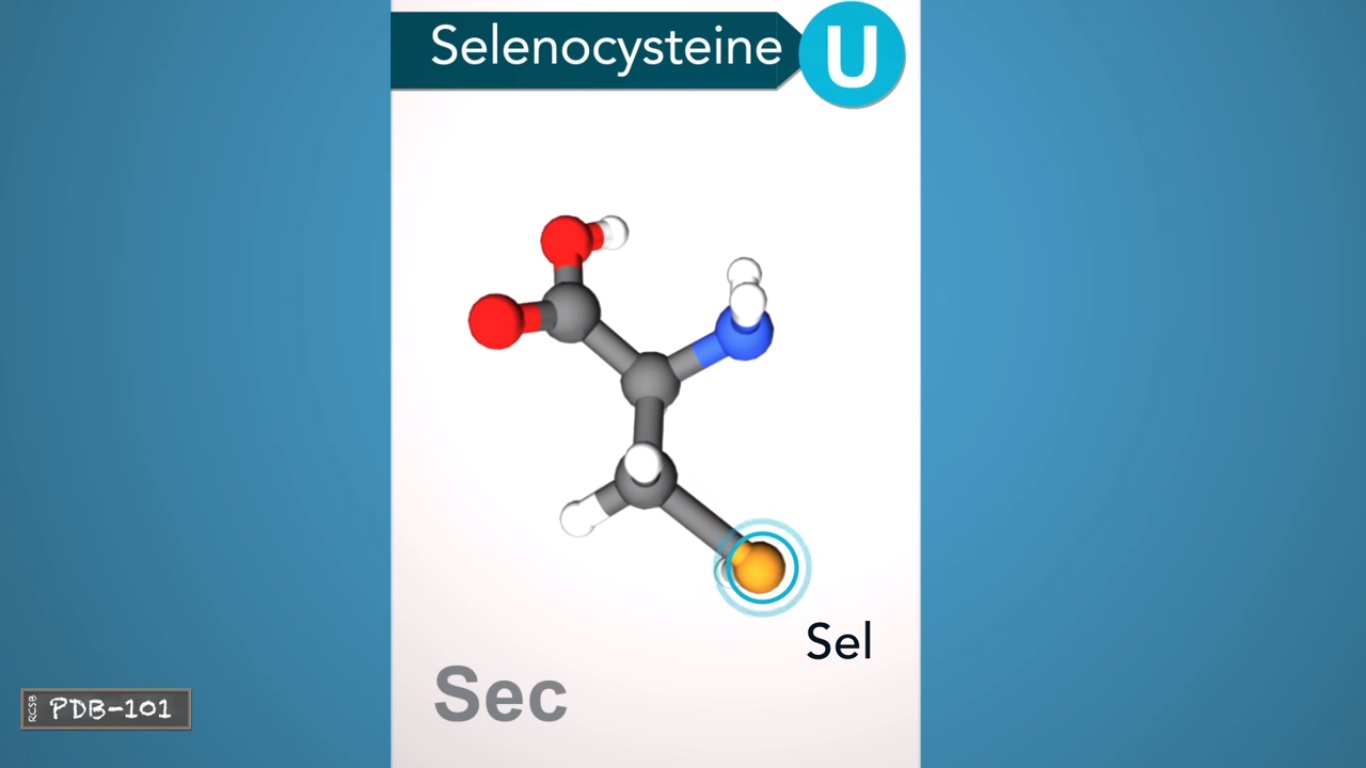
selenocysteine is the only standard amino acid that contains a Selenium atom.
These atoms forming a amino group a carboxyl and a side chain all attached to a central carbon atom.
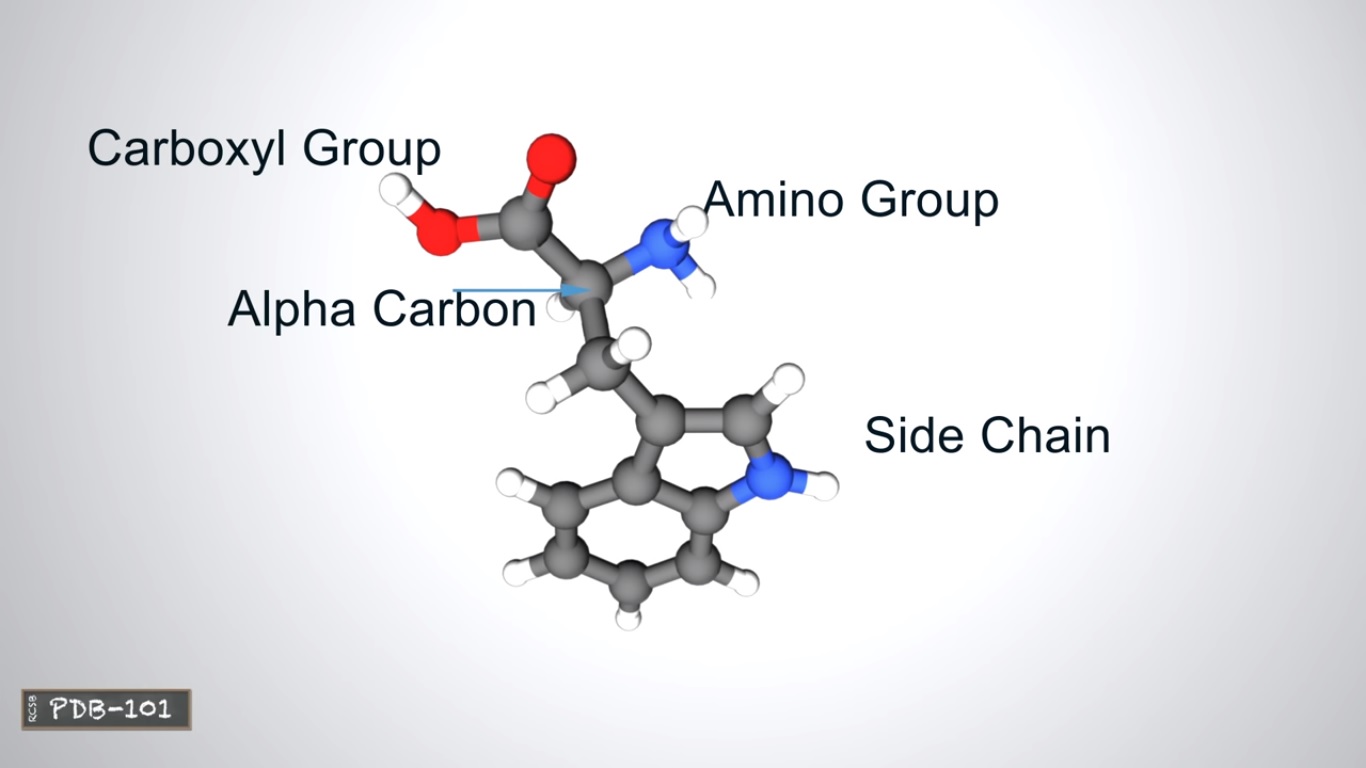
The side chain determines an amino acids properties and is the only part that varies from amino acid to amino acid(as shown in the above 21 BCAA)
Hydrophobic amino acids have carbon rich side chains which don't interact well with water.
I'd Philip or polar amino acids interact well with water.
Charging me of assets interact with oppositely charged amino acids or with other molecules.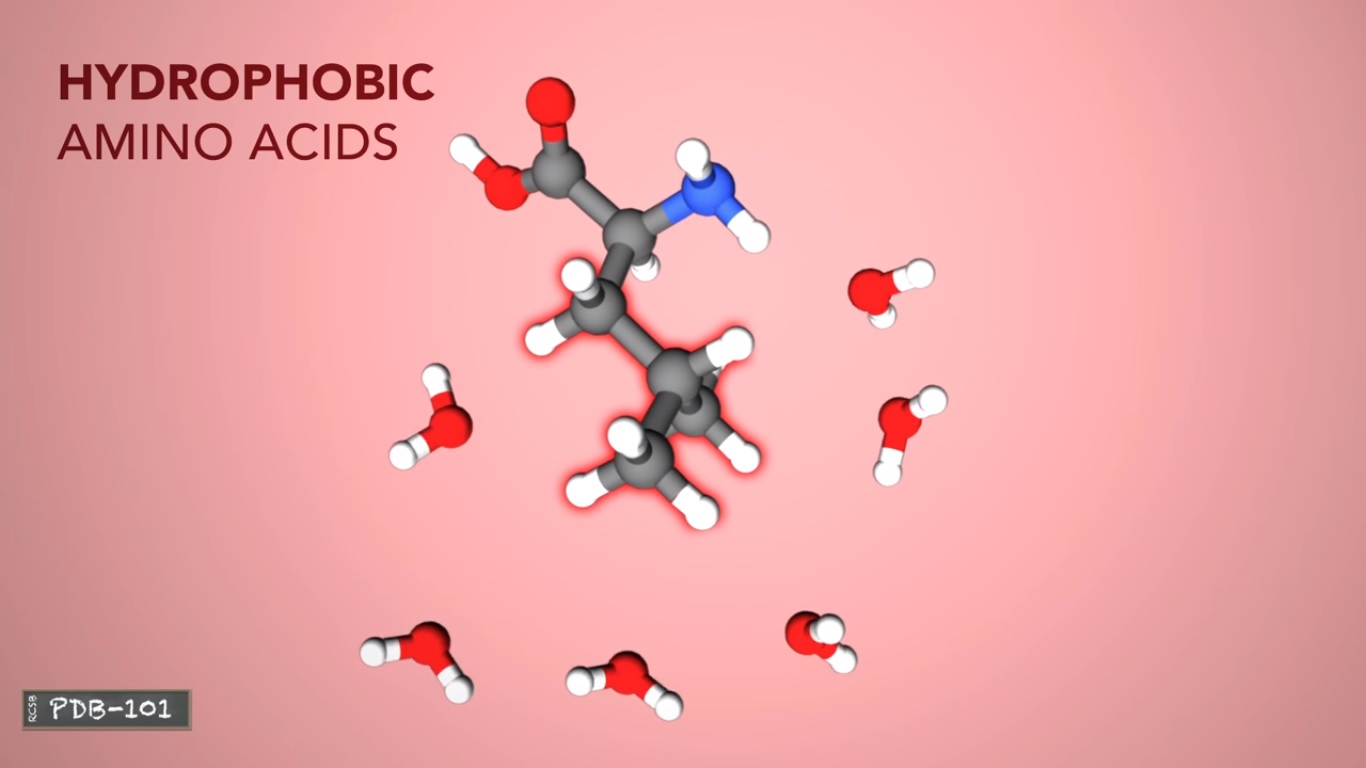
Primary structure.
The primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids.
Has included by DNA.
The amino acids in a protein are joined by peptide bonds which link the amino group of one amino acid to the carboxylate of another a water molecules released each time a peptide bond is formed.
This link series of carbon nitrogen oxygen atoms is the protein backbone.
Protein chains often fold into two types of secondary structures alpha helices and data sheets.
An alpha helix is a right handed coil stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the I mean and carboxylates of nearby amino acids.
Beta sheets are formed when hydrogen bonds stabilize two or more adjacent strands of amino acids.
The tertiary structure of a protein is the three dimensional shape of the protein chain.
The shape is determined by the characteristics of the amino acids making up the chain.
Many proteins form globular shapes with hydrophobic side chain sheltered on the inside away from surrounding water molecules.
Membrane bound proteins have hydrophobic amino acids cluster together on their exteriors so that hydrophobic side chains can interact with the lipids in the membrane.
Charged amino acids allow proteins to interact with molecules of complementary charges.
But.
The functions of many proteins rely upon their three dimensional shapes for example.
In the globe and forms a pocket to hold team a small molecule with an iron atom in the center.
That binds to oxygen.
Quaternary structure.
Two or more polypeptide chains can come together to form one functional molecule with several subunits.
The four subunits of hemoglobin cooperate so the complex can more easily pick up oxygen in the lungs.
And release it in the body.
Different visual representations of proteins can give us visual clues about protein structure and function.
This space filling diagram shows all of the atoms that make up this protein.
This representation.
Called a ribbon or cartoon diagram shows the organization of the protein backbone and highlights off he'll sees.
The surface representation shows the areas on the protein.
That are accessible to water molecules.
Most proteins are smaller than the wavelength of light for example the hemoglobin molecule is about six point five nanometers in size.
For.
In the globe and is found in high concentration in red blood cells.
A typical red blood cell contains about two hundred and eighty million hemoglobin molecules.
The three dimensional shapes of proteins determine their function.
The flexible arms of antibodies protect us from disease by recognizing and binding to pathogens and targeting them for destruction by the immune system.
The hormone insulin is a small stable protein that can easily maintain its shape.
While traveling through the blood to regulate blood glucose level.
Alpha amylase is an enzyme that begins digestion of starch is in our saliva.
The calcium pump is aided by magnesium.
And powered by A. T. P. to move calcium ions back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum after each muscle contraction.
Sheraton is a spherical protein with channels that allow iron atoms to enter and exit depending upon organisms needs on the inside certain forms a hollow space with iron atoms attached to the inner wall.
It's in stores iron in a non toxic form.
Collagen forms a strong triple helix that is used throughout the body for structural support.
Collagen molecules conform along grated fibrils.
Which aggregate form collagen fibers.
This type of collagen is abundant in skin and tendons.
Learn more about the functions in three D. structures proteins and other molecular machines at the RCS be protein data.
Related Posts
Comments
Write Comment
💬 Need help? Chat with us